Aus aktuellem Anlass schreibe ich hier einmal etwas zu gängigen WLAN/WiFi-Problemen — wie erkenne ich sie, und wie beseitige ich sie.
(Der aktuelle Anlass ist, dass hier bei uns im Ort endlich die lang ersehnten Aktivierungen unserer Glasfaser/FTTH-Anschlüsse von “Deutsche Glasfaser” erfolgt sind. Daher häufen sich diese Fragen bei mir und anderen Mitgliedern unserer Bürgerinitiative.)
Zunächst einmal ein bisschen Grundlagenwissen, (hoffentlich) so erklärt dass es auch Menschen verstehen können, die nicht Elektrotechnik studiert haben. 😉
WLAN ist ein “shared medium”, ein “geteiltes (Übertragungs-) Medium”, d. h. die maximal erreichbare Geschwindigkeit wird zwischen allen Teilnehmern eines WLANs aufgeteilt. Führt also gerade eine Station im Netz einen großen Download mit hoher Geschwindigkeit durch, dann werden die anderen Stationen im Netz entsprechend ausgebremst.
WLAN kann auf zwei Frequenz”bändern” stattfinden, dem “alten” 2,4 GHz-Band und dem (relativ) neuen 5 GHz-Band. Client (also Laptop, Handy…) und Router (Access Point) müssen jeweils beide das 5 GHz-Band beherrschen, damit dieses benutzt werden kann (Stichworte sind 802.11a oder 802.11ac, bei 802.11n kann es sich sowohl um 2,4 als auch 5 GHz handeln). Als “Access Point” bezeichnet man das WLAN-Radio in einem Router, es gibt auch separate Access Points, die nur der Koppelung von drahtlosen Stationen an ein drahtgebundenes LAN dienen.
Auf Grund seiner hohen Frequenzen ist das 5 GHz-Band “kurzwelliger”, dadurch ist seine Reichweite gegenüber dem 2,4 GHz-Band begrenzt (es durchdringt nicht so leicht Decken und Wände), was durchaus gewisse Vorteile hat, doch dazu später.
Die gesamten 2,4 bzw. 5 GHz-Bänder werden in so genannte “Kanäle” aufgeteilt, damit sich mehrere Betreiber eines WLANs nicht “ins Gehege kommen” und jeweils einen eigenen Kanal zum Übertragen haben. In eng besiedelten Gegenden, z. B. in Innenstadtbereichen, aber auch durchaus hier bei uns im Neubaugebiet, kommt es oft vor, dass sich Kanäle überlappen. Dies ist unbedingt zu vermeiden, weil dies die Übertragungsrate für alle(!) beteiligten WLANs reduziert.
Um festzustellen, ob diese Situation bei sich selbst vorliegt, sollte man ein Tool wie den kostenlosen WiFiAnalyzer benutzen. Im Bereich “Channel Graph” kann man dann einen Graphen wie den Folgenden sehen: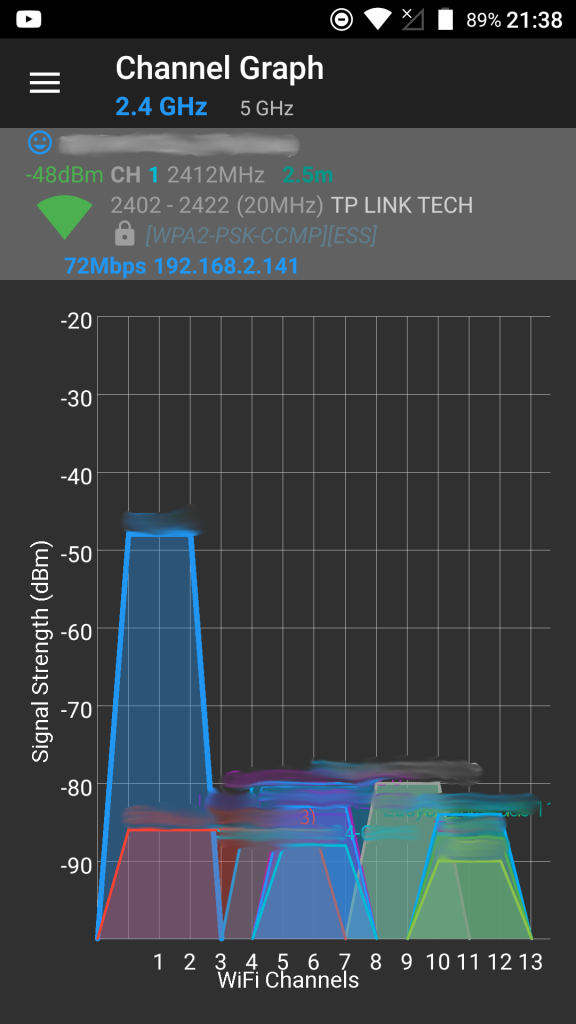
Was sagt uns jetzt dieser Graph? Zum einen sehen wir oben in blau, dass hier das 2,4 GHz-Band betrachtet wird (man kann dort auch auf das 5 GHz-Band umschalten, um dieses zu betrachten). Unten sieht man die Kanäle im 2,4 GHz-Band, in Deutschland sind 1-13 erlaubt.
(An dieser Stelle die dringende Warnung, keine verbotenen Kanäle zu benutzen. Dies kann Störungen verursachen. Der Verursacher haftet für alle entstehenden Kosten, das kann schnell in die Tausende Euro gehen, plus eine empfindliche Geldbuße nach sich ziehen!)
Die einzelnen farbigen, mehr oder weniger “hohen” Buckel sind die Frequenzbänder, die die einzelnen WLANs belegen. Wie bereits gesagt sollten sich diese idealerweise nicht überlappen. Die “Höhe” der Buckel zeigen die Signalstärke an. Je höher der Buckel, desto stärker das Signal. Wenn das eigene WLAN von einem oder mehreren fremden WLAN(s) überlappt wird, dann ist der Einfluss umso geringer, je schwächer das oder die fremde(n) WLAN(s) ist/sind.
Idealerweise spricht man sich als Nachbarn gegenseitig ab, wer welchen Kanal belegt, damit eben nicht solche Überlappungen zu Stande kommen. Der Bereich “Access Points” in der oben empfohlenen Android-App ist hier sehr hilfreich. Wenn man sich auf der eigenen Straße bewegt, kann man an der Signalstärke relativ schnell erkennen, wo welches WLAN “zu Hause ist”.
Ein Access Point benutzt zu jedem Zeitpunkt nur einen bestimmten Kanal (bzw. mehrere Kanäle gebündelt, um den Durchsatz zu erhöhen). Viele Access Points sind ab Werk so eingestellt, dass sie sich automatisch den “besten” Kanal suchen. Ich persönlich rate dazu, den eigenen Access Point fest auf einen bestimmten Kanal einzustellen und diesen mit den Nachbarn zu koordinieren, um besagte Überlappung zu verhindern.
Eine weitere Einstellung sollte auch nach Möglichkeit modifiziert werden. Viele Access Points erlauben die Einstellung der Sendeleistung. Diese sollte möglichst konservativ gewählt werden derart, dass der Access Point die eigenen Geräte gerade noch gut erreicht, jedoch nicht viel weiter sendet. Sonst kommt eben die erwähnte Überlappung zu Stande, die man gerne vermeiden möchte. Access Points, die so eine Überlappung feststellen, können dann durchaus ihre Sendeleistung (in vorgegebenem Rahmen) erhöhen, um den anderen zu “übertönen”. Dies geschieht, damit wieder ein gewisser “Signal-Rauschabstand” gewährleistet ist, um das (eigene) Signal vom “Rauschen” (dem Fremdsignal) sauber trennen zu können.
Um Überlappungen zu reduzieren oder zu vermeiden kann man auch die Kanalbreite reduzieren. In dem obigen Screenshot sieht man hauptsächlich WLANs, die eine Kanalbreite von 20 MHz benutzen. Wie bereits kurz erwähnt kann man die Kanalbreite erhöhen, um einen größeren Durchsatz zu erzielen. Das rote WLAN im obigen Diagramm benutzt eine Kanalbreite von 40 MHz. Dadurch kommen entsprechend viele Überlappungen zu Stande.
Reduziert man die Kanalbreite, so vermeidet man ggf. eine Überlappung vollständig oder reduziert zumindest die Anzahl der überlappenden Netze. Obwohl dadurch die (unter Idealbedingungen) maximal erzielbare Kanalbreite reduziert wird, wird man wahrscheinlich in der Praxis feststellen, dass der Betrieb nun wesentlich stabiler ist und die Transferraten womöglich höher sind als vorher!
Alternativ, und das ist meine dringendste Empfehlung, kann man auf das 5 GHz-Band ausweichen. Wenn alle eigenen Geräte dieses unterstützen, dann empfehle ich, das 2.4 GHz-Band komplett abzuschalten. Dies kommt auch einem Bluetooth-Betrieb zu Gute, der auf einem ähnlichen Frequenzbereich stattfindet. Das 5 GHz-Band bietet deutlich höhere Transferraten und den zusätzlichen Vorteil, dass es nicht so “überlaufen” ist wie das 2,4 GHz-Band. Dies ist zum einen der geringeren Verbreitung geschuldet, zum anderen aber auch der deutlich geringeren Durchdringung und damit Reichweite der 5 GHz-Wellen.
Hier noch einmal ein Screenshot von meiner eigenen Situation, diesmal im 5 GHz-Band:
 Man sieht, dass bei mir überhaupt nur zwei Netze im 5 GHz-Band sichtbar sind. Mein eigenes (welches man an Hand der Signalstärke sehr einfach identifizieren kann) und ein fremdes. Der Signal-Rauschabstand zwischen diesen beiden Netzen ist jedoch so groß, dass das Fremdnetz quasi nicht stört. Ich erreiche hier Transferraten von mehr als 200 MBit/s in beide Richtungen (beim Senden und beim Empfangen) mit Stationen, die das unterstützen.
Man sieht, dass bei mir überhaupt nur zwei Netze im 5 GHz-Band sichtbar sind. Mein eigenes (welches man an Hand der Signalstärke sehr einfach identifizieren kann) und ein fremdes. Der Signal-Rauschabstand zwischen diesen beiden Netzen ist jedoch so groß, dass das Fremdnetz quasi nicht stört. Ich erreiche hier Transferraten von mehr als 200 MBit/s in beide Richtungen (beim Senden und beim Empfangen) mit Stationen, die das unterstützen.
So, das soll es gewesen sein. Ich hoffe, dieser Blog-Post nutzt dem einen oder dem anderen. Ich würde mich in diesem Fall über einen Kommentar hier in meinem Blog sehr freuen. Fragen werde ich gerne beantworten. Sollte ich etwas vergessen haben, werde ich den Post noch entsprechend ergänzen.
Viel Erfolg beim Optimieren Eurer WLANs!